Tooth extractions
Our comfortable extraction techniques and sedation options eliminate pain and anxiety, with most patients returning to normal activities within 48-72 hours.
What is a tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction is a common oral surgery procedure in which a tooth is removed from its socket in the jawbone. While our primary goal is to preserve natural teeth whenever possible, extraction is sometimes the best choice for protecting your oral and overall health.
Extractions may be straightforward or complex, depending on the tooth’s position and condition. Our team ensures your comfort, safety, and understanding at every step of the process, using advanced techniques and equipment to provide a smooth experience.
Tooth extractions may be recommended for a variety of clinical reasons, including:
- Extensive decay or infection: When a tooth is too damaged for restoration, removal may prevent the spread of infection to surrounding teeth or bone.
- Advanced periodontal disease: Gum disease can weaken the structures supporting a tooth, leading to looseness and eventual loss.
- Impacted teeth: Teeth that are stuck beneath the gums—often wisdom teeth—can cause pain, infection, or damage to neighboring teeth.
- Orthodontic purposes: Removing certain teeth may be necessary to create space for effective alignment in orthodontic treatment.
- Fractured teeth: In some cases, a tooth that is broken below the gum line cannot be repaired and must be removed.
- Prosthetic or implant planning: Extraction may be part of preparing the mouth for full or partial dentures, or for implant placement.
Each recommendation is based on thorough diagnostic imaging and clinical assessment to ensure that removal is the most appropriate treatment.
Types of tooth extractions
There are two primary methods of extraction used in our practice:
Simple extraction
Used when the tooth is visible and fully erupted. The area is numbed with local anesthesia, and the tooth is gently loosened and removed using specialized instruments.
Surgical extraction
Required for teeth that are impacted, broken, or located beneath the gum line. This approach may involve a small incision in the gum, bone removal, or sectioning the tooth into smaller pieces for safe removal.
Surgical extractions are commonly used for wisdom teeth, broken molars, or teeth with complex root structures. We will explain the procedure in detail so you know exactly what to expect.
What to expect during the procedure
We strive to make every extraction as comfortable and stress-free as possible. Here’s what you can typically expect:
Anesthesia
The area will be thoroughly numbed using local anesthetic. If you’re undergoing a surgical extraction or experiencing anxiety, sedation options are available.
Learn more
Removal
Using controlled and gentle techniques, we remove the tooth while minimizing disruption to surrounding bone and tissue.
Site management
Once the tooth is removed, the socket is cleaned, and sutures may be placed if necessary. Gauze will be applied to help control bleeding and encourage clot formation.
You’ll receive detailed instructions on how to care for the extraction site and support proper healing after the procedure.
Sedation options
For many patients, oral surgery can cause anxiety. We offer several sedation options to ensure your comfort during the procedure:
- Local anesthesia: Always used to numb the treatment area.
- Nitrous oxide (laughing gas): Provides a sense of relaxation during the procedure while keeping you awake and aware.
- IV sedation: A deeper form of sedation administered intravenously, often used for more complex extractions or patients with dental anxiety. Most patients have little or no memory of the procedure. To learn more about IV Sedation click here.
We will discuss the most appropriate sedation option for your needs during your consultation.
Recovery & aftercare
Recovery after a tooth extraction typically involves mild discomfort and swelling, which are manageable with proper care. Key guidelines include:
- Bleeding: Bite on gauze for 30–60 minutes to control initial bleeding. Some minor oozing may persist for several hours.
- Swelling & pain: Swelling and pain are common and both usually peak within 48-72 hours, although this is dependent on many factors including the complexity of the extraction and the number of teeth extracted.
- Diet: Stick to soft foods (soups, smoothies, yogurt) and avoid hot, spicy, or hard foods for several days. Stay hydrated, but avoid using straws.
- Oral hygiene: Avoid brushing near the extraction site for the first 24 hours. After that, rinse gently with warm salt water and resume brushing carefully.
- Activity: Rest and avoid strenuous physical activity for the first 24–48 hours to promote healing and prevent complications.
Most patients feel significantly better within a few days. Full healing of the extraction site may take several weeks.
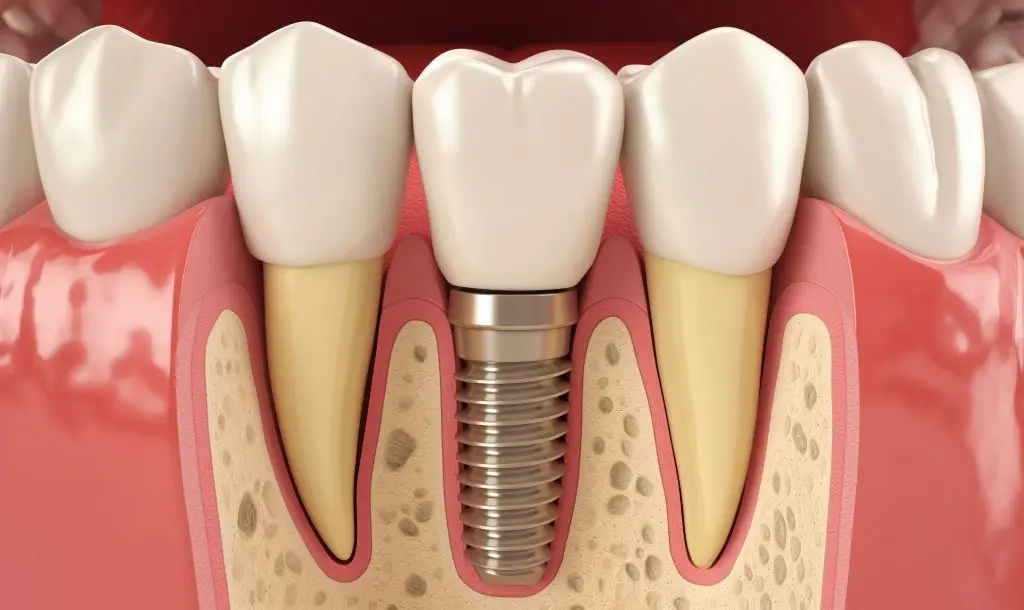
Replace your extracted tooth with a dental implant
After a tooth is extracted, it’s important to consider replacement—especially if the removed tooth is not a wisdom tooth. A missing tooth can lead to:
- Bone loss in the jaw where the tooth once was
- Shifting of adjacent teeth, which may affect bite alignment
- Changes in facial structure over time
- Difficulty chewing or speaking clearly
One of the most effective and long-lasting solutions is a dental implant. A dental implant is a small titanium post placed into the jawbone to act as an artificial tooth root. After healing, a crown is placed on top to restore natural function and appearance.
Benefits of dental implants
- Preservation of jawbone structure and prevention of bone loss
- Permanent, stable tooth replacement that looks and feels like your natural tooth
- No impact on neighboring teeth, unlike dental bridges
- Improved chewing ability and overall oral function
- Aesthetic enhancement and support for facial features
Start planning for a dental implant
In many cases, we can begin planning for a dental implant at the time of extraction or shortly afterward. We will discuss your options and timing for tooth replacement as part of your personalized treatment plan.